Python is an amazing and simple language. Its actually a beast when it comes to complex coding now lets learn the basics.
Installation Process:
Before going into python coding lets see how to install it to your system. The below video shows the installation process for Windows and Linux operating system.
Math operators:
Well when it comes to basic math operations you can consider the python idle to be similar to a calculator.
Syntax:
Addition – x+y – Sum of x and y
Subtraction – x-y – Difference between x and y
Multiplication – x*y – Product of x and y
Division – x/y – Quotient of x and y
Reminder – x%y – Reminder of x and y
Example:
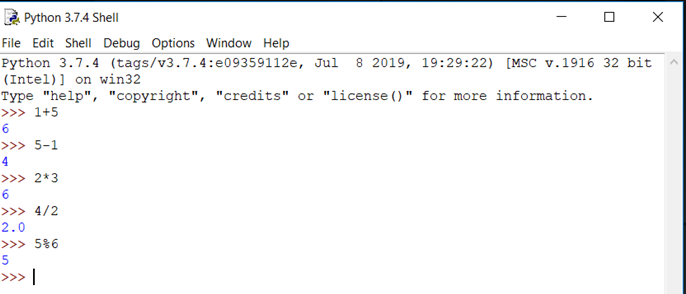
Now that we have seen the basic operations lets see what other math operations python can do
-x – Changes sign of x
+x – Identity of x
x//y – Quotient from floor division of x and y
x**y – x to the y power
(FYI : -x and +x are called unary operations cause only one operand is used)
Example:
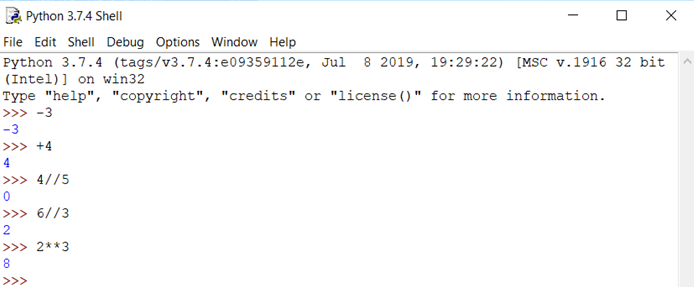
Comparison Operators:
They are used to compare the two values given to them and it gives the result in Boolean form
Consider a = 5 and b = 10
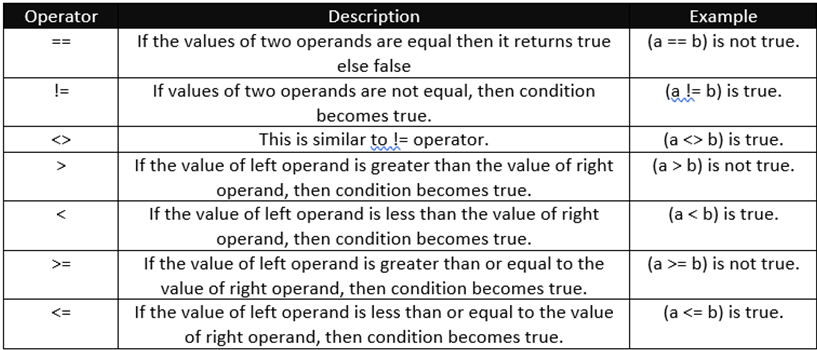
Assignment Operators:
An assignment operator is the operator used to assign a new value to a variable.
Consider a = 5 and b = 10
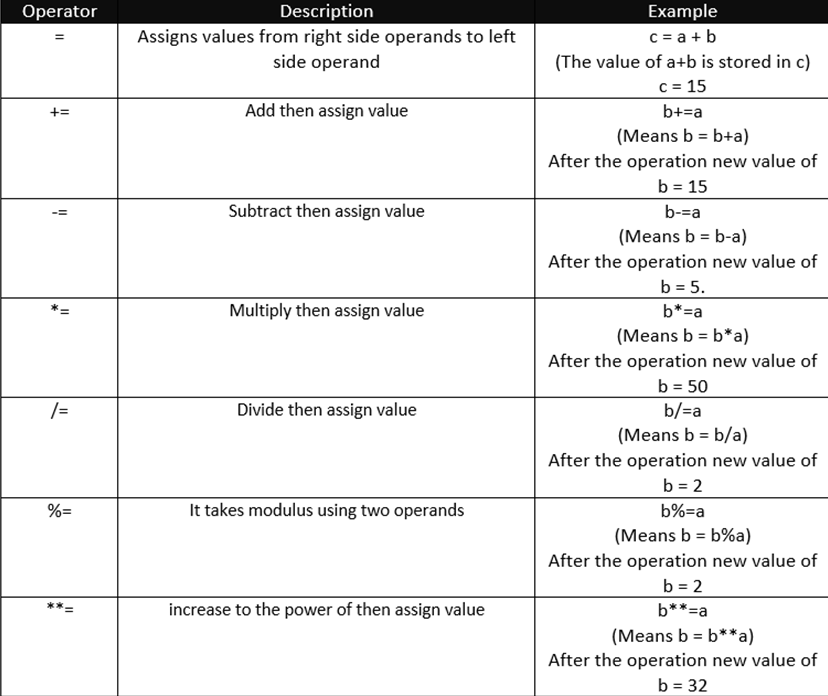
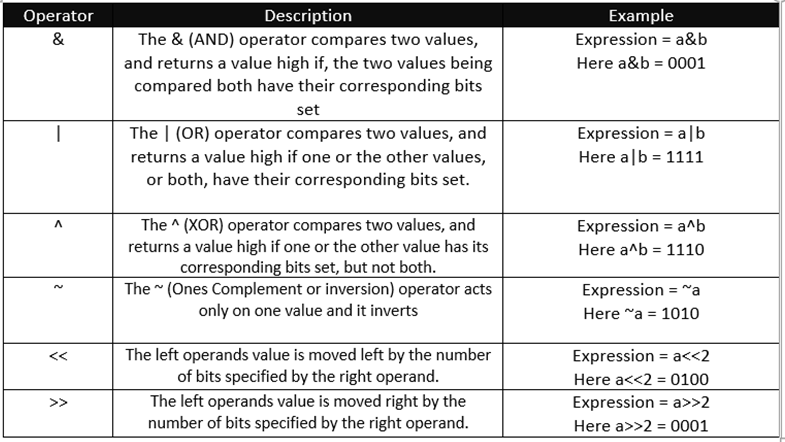
Bitwise operator:
Bitwise operator is an operator used to perform bitwise operations on bit patterns or binary numerals that involve the manipulation of individual bits.
Assume a = 5 and b = 11. Now the binary format is a = 0101 and b = 1011

Python Logical Operators:
A logical operation is a special symbol or word that connects two or more phrases of information. It is most often used to test whether a certain relationship between the phrases is true or false.
Consider a = 5 and b = 10
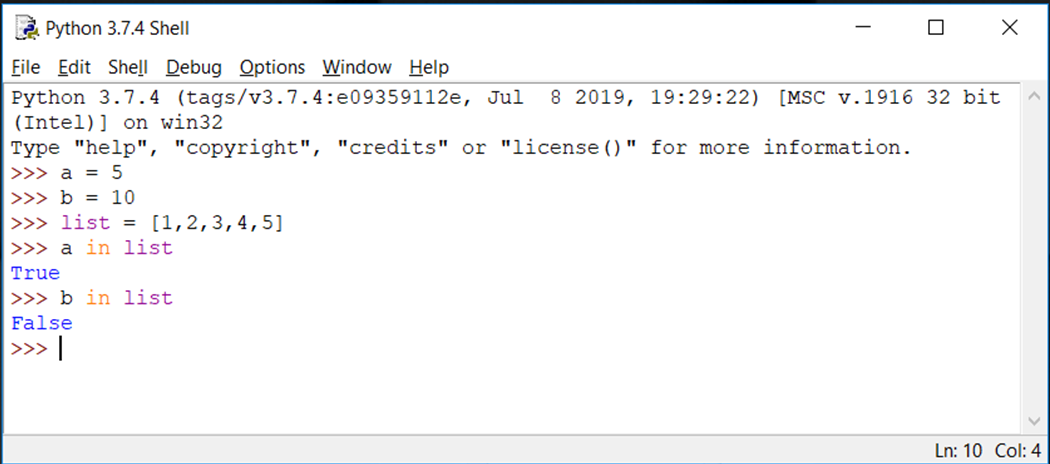
Python Membership Operators
Operator : in
Evaluates to true if it finds a variable in the specified sequence and false otherwise.
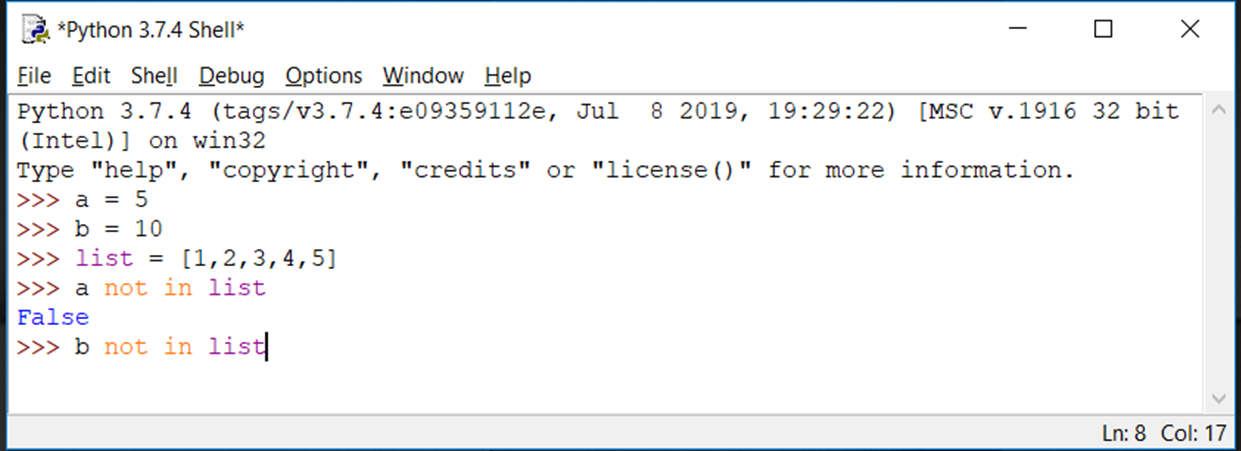
Operator : not in
Evaluates to true if it does not finds a variable in the specified sequence and false otherwise. Operator :
not in Operator :
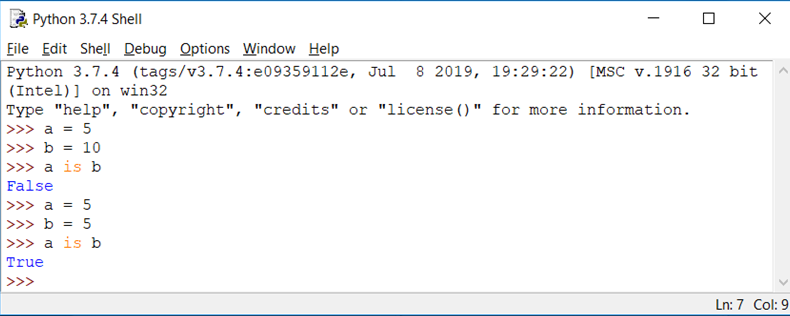
Identity Operators:
Operator : is
Evaluates to true if the variables on either side of the operator point to the same object and false otherwise.
Operator : is not
Evaluates to false if the variables on either side of the operator point to the same object and true otherwise.
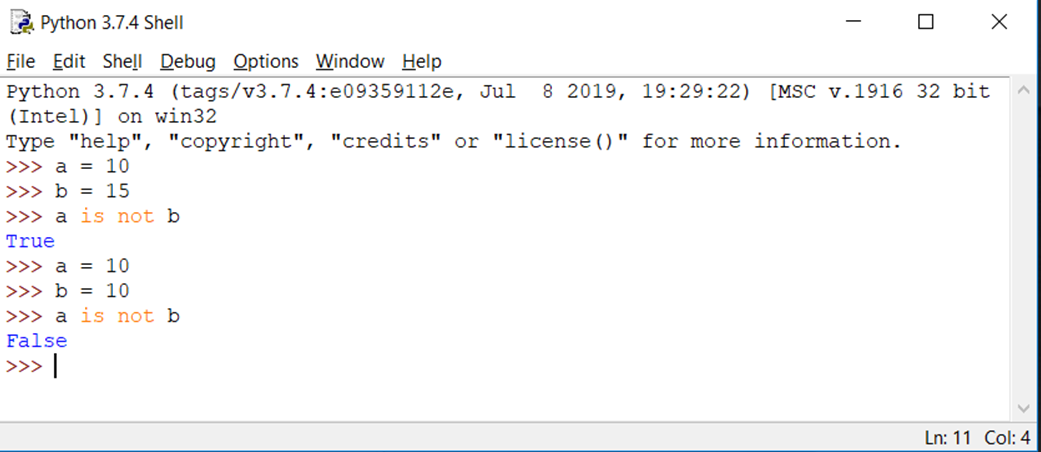
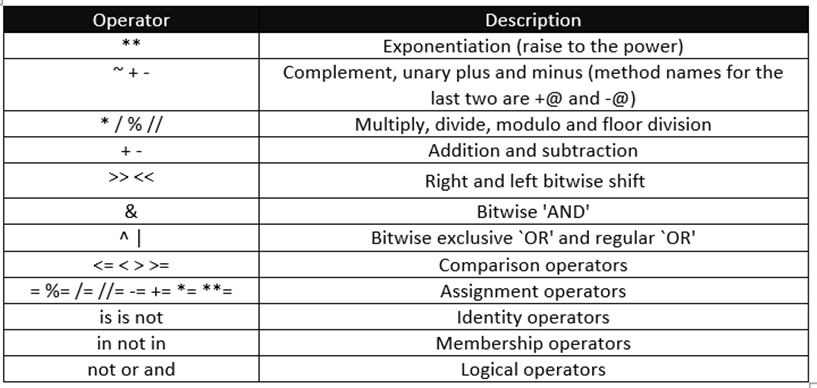
Operator Precedence:
Operator precedence affects how an expression is evaluated. Its similar to math where the given expression will be executed in the order of precedence. The table of precedence is given below. Operations with the higher precedence are mentioned in the top as we go down the table it decreases.
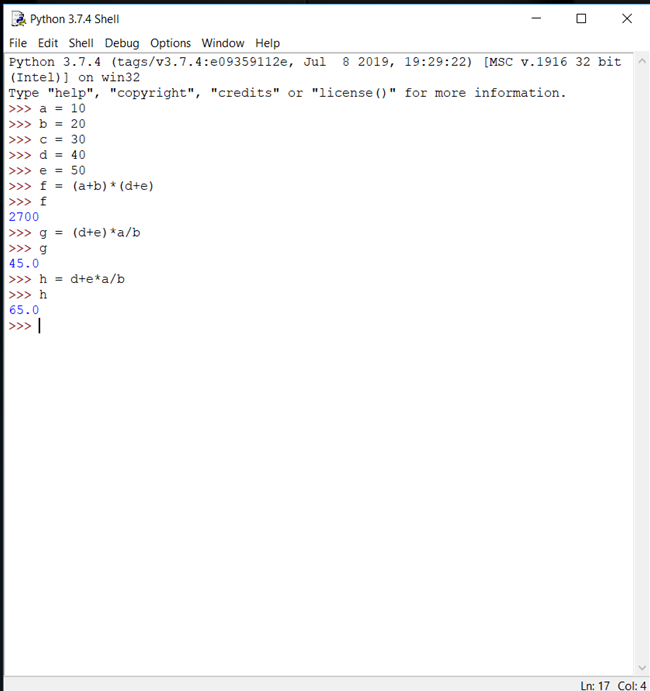
Example:
THE END (not really!)
We have come to the end of this blog, but its still the beginning of the python in the further blogs I’ll keep you updated, please subscribe to the blog!!
Video & editing credits : Arcot Gautham
Author : Nivedita.M

